-
LAW OF SUPPLY
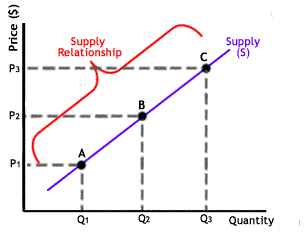
Supply means the goods offered for sale at a price during a specificperiod of time. It is the capacity and intention of the producers to producegoods and services for sale at a specific price.The supply of a commodity at a given price may be defined as theamount of it which is actually offered for sale per unit of time at thatprice. The law of supply establishes a direct relationship between priceand supply. Firms will supply less at lower prices and more at higherprices. “Other things remaining the same, as the price of commodityrises, its supply expands and as the price falls, its supply contracts”.
Best SSC CGL Coaching Centre in Vijayawada - SSC Staff Selection Commission Training Centre in Vijayawada - SSC CGL Coaching Centre - Best SSC Trining Centre - SSC CHSL Coaching Centre in vijayawada - SSC JE Coaching centre
Elasticity of Supply
The law of supply tells us that quantity supplied will respond to achange in price. The concept of elasticity of supply explains the rate ofchange in supply as a result of change in price. It is measured by theformula mentioned below
Elasticity of supply = Proportionate change in quantity supplied/Proportionate change in price
FORMS OF MARKET AND PRICE DETERMINATION
Market: Market is a place in which buyers and sellers come into contact for the purchase and sale of goods and services.
Market structure: refers to number of firms operating in an industry, nature of competition between them and the nature of product.
Types of market
a) Perfect competition.
b) Monopoly.
c) Monopolistic Competition
d) Oligopoly.
a) Perfect competition: refers to a market situation in which there are large number of buyers and sellers. Firms sell homogeneous products at a uniform price.
b) Monopoly market: Monopoly is a market situation dominated by a single seller who has full control over the price.
c) Monopolistic competition: It refers to a market situation in which there are many firms who sell closely related but differentiated products.
d) Oligopoly: is a market structure in which there are few large sellers of a commodity and large number of buyers.Best SSC CGL Coaching Centre in Vijayawada - SSC Staff Selection Commission Training Centre in Vijayawada - SSC CGL Coaching Centre - Best SSC Trining Centre - SSC CHSL Coaching Centre in vijayawada - SSC JE Coaching centre
Features of perfect competition:
1. Very large number of buyers and sellers.
2. Homogeneous product.
3. Free entry and exit of firms.
4. Perfect knowledge.
5. Firm is a price taker and industry is price maker.
6. Perfectly elastic demand curve (AR=MR)
7. Perfect mobility of factors of production.
8. Absence of transportation cost.
9. Absence of selling cost.
Features of monopoly:
1. Single seller of a commodity.
2. Absence of close substitute of the product.
3. Difficulty of entry of a new firm.
4. Negatively sloped demand curve(AR>MR)
5. Full control over price.
6. Price discrimination exists
7. Existence of abnormal profit.
Features of monopolistic competition
1. Large number of buyers and sellers but less than perfect competition.
2. Product differentiation.
3. Freedom of entry and exit.
4. Selling cost.
5. Lack of perfect knowledge.
6. High transportation cost.
7. Partial control over price.
Main features of Oligopoly.
1. Few dominant firms who are large in size
2. Mutual interdependence.
3. Barrier to entry.
4. Homogeneous or differentiated product.
5. Price rigidity.
Features of pure competition
1. Large number of buyers and sellers.
2. Homogeneous products.
3. Free entry and exit of firm.
What are selling cost?
Ans.: Cost incurred by a firm for the promotion of sale is known as selling cost. (Advertisement cost)
What is product differentiation?
Ans: It means close substitutes offered by different producers to show their output differs from other output available in the market. Differentiation can be in colour, size packing, brand name etc to attract buyers.
What do you mean by patent rights?
Ans:- Patent rights is an exclusive right or license granted to a company to produce a particular output under a specific technology.
What is price discrimination?
Ans: - It refers to charging of different prices from different consumers for different units of the same product.Best SSC CGL Coaching Centre in Vijayawada - SSC Staff Selection Commission Training Centre in Vijayawada - SSC CGL Coaching Centre - Best SSC Trining Centre - SSC CHSL Coaching Centre in vijayawada - SSC JE Coaching centre

